Sustainable Watershed Management
Through IoT-Driven Artificial Intelligence
Sustainable Watershed Management
Through IoT-Driven Artificial Intelligence
Water resource contamination substantially threatens the environment. Rapid identification of chemicals and their emission sources in watersheds is crucial for sustainable water resources management. Despite studies on the measurement of micropollutants in the water resources around Europe, efficient utilization of the data in decision-making to protect water resources from detrimental chemical pollution is currently not available. Novel Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, coupled with advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) strategies, may provide faster and more efficient responses to these challenges in real-time reactions as well as long-term planning.
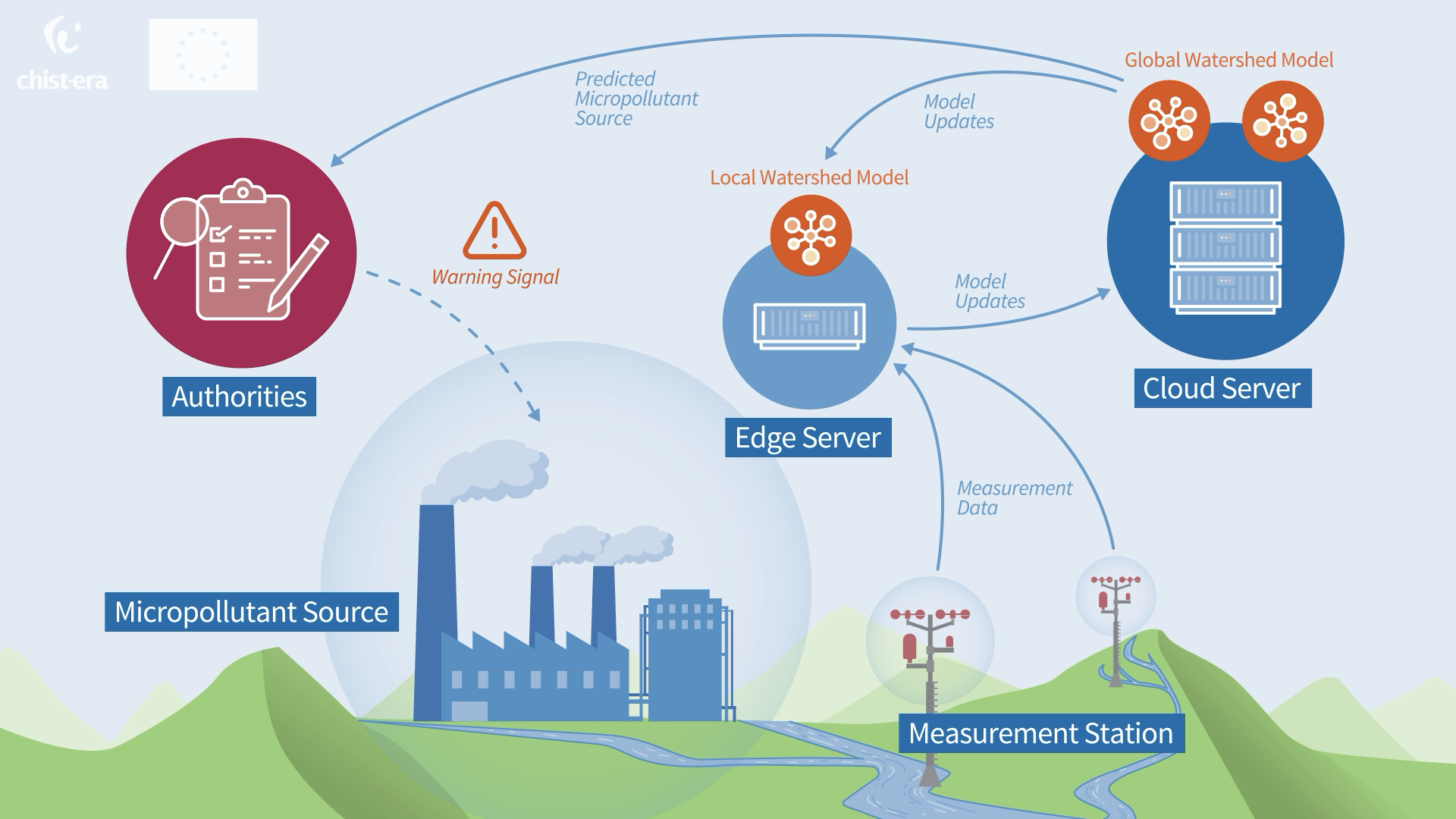
The proposed solution aims at providing: better understanding and near real-time response to pollution incidents; better prediction of pollution spread and improved response for mitigation of effects in the long run; data-driven AI life-long learning and evolution of the algorithm. The primary outcome would be an integrated decision support system utilizing micropollutant measurements along with real-time collected hydrodynamic and meteorological data of a watershed for sustainable water quality management. Since micropollutants are related to emission sources and are resistant to degradation, they are good indicators of pollution and fingerprints of the pollution sources.
Our approach is based on introducing and combining novel technologies in improving water pollution management in several critical phases. First of all, we rely on an advanced, scalable IoT technology that adapts to the considered problem's specific needs through a novel mechanism called viscoelasticity. Therefore, we obtain desirable data from the locations and at the time that is optimized for further data analysis. Then, we introduce a novel methodology for creating a more accurate hybrid model integrating the expert-based physical environment model and data-driven, evidence-based techniques. To that end, we introduce a novel graph-based functional representation of data that captures affinities and dependencies among data streams more efficiently.

Call Topic: Novel Computational Approaches for Environmental Sustainability (CES), Call 2019
Start Date: March 2021 (36 months)
Funding Support: 1,157,341 €
This project is supported by the CHIST-ERA grant CHIST-ERA-19-CES-005, by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF), by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF), by the Academy of Finland (AKA), and by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK).
Sürmeli Bilir, T. (2024). Biological and chemical transformation of hexamethoxymethyl melamine (Thesis No: 849883) [Master's thesis, Boğaziçi University]. CoHE Thesis Center. [URL]
Ahkola, H., Kotamäki, N., Siivola, E., Tiira, J., Imoscopi, S., Riva, M., Tezel, U., & Juntunen, J. (2024). Uncertainty in environmental micropollutant modeling. Environmental Management. DOI: 10.1007/s00267-024-01989-z
Catalfamo, A., Aral, A., Brandic, I., Deelman, E., & Villari, M. (2024). Machine Learning Workflows in the Computing Continuum for Environmental Monitoring. 24th International Conference on Computational Science, ICCS (accepted).
Ahmad, S., Uyanik, H., Ovatman, T., Sandikkaya, M. T., De Maio, V., Brandic, I., & Aral, A. (2023). Sustainable Environmental Monitoring via Energy and Information Efficient Multi-Node Placement. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3303124
Ilager, S., Toosi, A. N., Jha, M. R., Brandic, I., & Buyya, R. (2023). A data-driven analysis of a cloud data center: statistical characterization of workload, energy and temperature. IEEE/ACM 16th International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing, UCC (pp. 1-10). DOI: 10.1145/3603166.3632137
Sari, T. T., Ahmad, S., Aral, A., & Secinti, G. (2023). Collaborative Smart Environmental Monitoring Using Flying Edge Intelligence. IEEE Global Communications Conference, GLOBECOM (pp. 5336-5341). DOI: 10.1109/GLOBECOM54140.2023.10436927
Ahmad, S. & Aral, A. (2023). Hierarchical Federated Transfer Learning: A Multi-Cluster Approach on the Computing Continuum. IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, ICMLA (pp. 1163-1168). DOI: 10.1109/ICMLA58977.2023.00174
Sayın, A. & Sandikkaya, M. T. (2023). A Reasoning Method to Interpret Fate of Pollutants on a Cyber-Physical River Model. International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering, UBMK (pp. 324-329). DOI: 10.1109/UBMK59864.2023.10286674
Ahkola, H. Juntunen, J. (2023). Tryptofaanin automaattimittaus jätevesipäästöjen tunnistamisessa. Vesitalous 6/2023. [Full Text] (in Finnish)
Aral, A. (2023). Neuromorphic Edge Intelligence for Rural Environmental Monitoring. ACM KDD 2023 Workshop Fragile Earth. [Full Text]
Luger, D., Aral, A., & Brandic, I. (2023). Cost-Aware Neural Network Splitting and Dynamic Rescheduling for Edge Intelligence. ACM International Workshop on Edge Systems, Analytics and Networking, EdgeSys (pp. 42-47). DOI: 10.1145/3578354.3592871
Herbst, S., De Maio, V., & Brandic, I. (2023). Streaming IoT Data and the Quantum Edge: A Classic/Quantum Machine Learning Use Case. European Conference on Parallel Processing, Euro-Par (pp. 177-188). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-50684-0_14
Hofstätter, D., Ilager, S., Lujic, I., & Brandic, I. (2023). Symed: Adaptive and online symbolic representation of data on the edge. European Conference on Parallel Processing, Euro-Par (pp. 411-425). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-39698-4_28
Tundo, A., Mobilio, M., Ilager, S., Brandić, I., Bartocci, E., & Mariani, L. (2023). An Energy-Aware Approach to Design Self-Adaptive AI-based Applications on the Edge. IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, ASE (pp. 281-293). DOI: 10.1109/ASE56229.2023.00046
Ilager, S., De Maio, V., Lujic, I., & Brandic, I. (2023). Data-centric Edge-AI: A Symbolic Representation Use Case. IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing and Communications, EDGE (pp. 301-308). DOI: 10.1109/EDGE60047.2023.00052
Aral, A., Esposito, A., Nagiyev, A., Benkner, S., Di Martino, B., & Bochicchio, M. A. (2023). Experiences in Architectural Design and Deployment of eHealth and Environmental Applications for Cloud-Edge Continuum. International Workshop on Cloud-Edge Continuum Projects and Initiatives, CCPI (pp. 136-145). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-28694-0_13
Can, B., Uyanik, H., & Ovatman, T. (2023). Gateway Placement in LoRaWAN Enabled Sensor Networks. International Conference on Sensor Networks, SENSORNETS (pp. 93-100). DOI: 10.5220/0011777000003399
Cranganore, S. S., De Maio, V., Brandic, I., Do, T. M. A., & Deelman, E. (2022). Molecular Dynamics Workflow Decomposition for Hybrid Classic/Quantum Systems. IEEE International Conference on e-Science (pp. 346-356). DOI: 10.1109/eScience55777.2022.00048
Ahmad, S. & Aral, A. (2022). FedCD: Personalized Federated Learning via Collaborative Distillation. Workshop on Distributed Machine Learning for the Intelligent Computing Continuum, DML-ICC (pp. 189-194). DOI: 10.1109/UCC56403.2022.00036
Ahmad, S. (2022). Communication and Energy Efficient Edge Intelligence. IEEE/ACM International Conference on Big Data Computing, Applications and Technologies, BDCAT (pp. 176-177). DOI: 10.1109/BDCAT56447.2022.00031
De Maio, V., Bermbach, D., & Brandic, I. (2022). TAROT: Spatio-Temporal Function Placement for Serverless Smart City Applications. IEEE/ACM International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing, UCC (pp. 21-30). DOI: 10.1109/UCC56403.2022.00013
Ilager, S., Fahringer, J., de Lima Dias, S. C., & Brandic, I. (2022). DEMon: Decentralized Monitoring for Highly Volatile Edge Environments. IEEE/ACM International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing, UCC (pp. 145-150). DOI: 10.1109/UCC56403.2022.00026
Peltonen, E., Ahmad, I., Aral, A., Capobianco, M., Ding, A. Y., Gil-Castiñeira, F., Gilman, E., Harjula, E., Jurmu, M., Karvonen, T., Kelanti, M., Leppänen, T., Lovén, L., Mikkonen, T., Mohan, N.,Nurmi, P., Pirttikangas, S., Sroka, P., Tarkoma, S., & Yang, T. (2022). The Many Faces of Edge Intelligence. IEEE Access. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3210584
De Maio, V., Aral, A., & Brandic, I. (2022). A Roadmap To Post-Moore Era for Distributed Systems. Workshop on Advanced tools, programming languages, and PLatforms for Implementing and Evaluating algorithms for Distributed systems, ApPLIED (pp. 30-34). DOI: 10.1145/3524053.3542747
Ding, A. Y., Peltonen, E., Meuser, T., Aral, A., Becker, C., Dustdar, S., Hiessl, T., Kranzl-müller, D., Liyanage, M., Magshudi, S., Mohan, N., Ott, J., Rellermeyer, J. S., Schulte, S., Schulzrinne, H., Solmaz, G., Tarkoma, S., Varghese, B., Wolf, L. (2022). Roadmap for Edge AI: A Dagstuhl Perspective. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 52(1), 28-33. DOI: 10.1145/3523230.3523235
Toczé, K., Schmitt, N., Kargén, U., Aral, A., & Brandić, I. (2022). Edge Workload Trace Gathering and Analysis for Benchmarking. IEEE International Conference on Fog and Edge Computing, ICFEC (pp. 34-41). DOI: 10.1109/ICFEC54809.2022.00012
Zhou, H., Aral, A., Brandic, I., & Erol-Kantarci, M. (2021). Multi-agent Bayesian Deep Reinforcement Learning for Microgrid Energy Management under Communication Failures. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3131719
D1.1 Project Management Plan [PUBLIC]
D1.2 Annual Activity Report 1 [PUBLIC]
D1.3 Annual Activity Report 2 [DUE 2023]
D1.4 Annual Activity Report 3 [DUE 2024]
D1.5 Quality Assurance and Risk Assessment Plan [PUBLIC]
D1.6 Data Management Plan [PUBLIC]
D1.7 Project Website and Promotional Materials [PUBLIC]
D2.1 Hydrogeographical and chemical parameters for water quality model (WQM) [PRIVATE]
D2.2 Consolidated Geo-Database [PUBLIC]
D4.1 Placement model [PRIVATE]
D4.2 Offline placement algorithm [PRIVATE]
D4.3 Models for communication technologies [PRIVATE]
D4.4 Adaptive communication channel selection method [PRIVATE]
